“Recognizing Symptoms of Gluten Intolerance”
Gluten earns its reputation as a silent executioner, causing persistent harm throughout the body. Therefore, to safeguard against gluten intolerance, it’s wise to check your body’s response.
“Gastrointestinal Challenges”

Gastrointestinal issues are commonly associated with symptoms such as nausea, bloating, diarrhea, stomach pain, and even constipation. However, individuals often misinterpret these symptoms, leading to misdiagnoses like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Consequently, this misdiagnosis can hinder proper treatment for those with gluten sensitivity.
“Weight Fluctuations and Metabolic Effects”
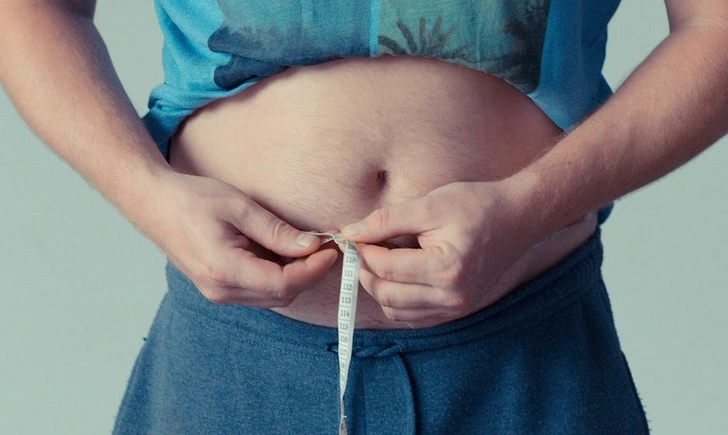
Moreover, gluten can lead to both weight loss and weight gain due to inflammatory processes at the cellular level and metabolic issues. Sudden weight changes may accompany other undesirable diseases but can be linked to gluten intolerance if combined with other malabsorption symptoms.
“Impact on Hormonal Balance”
Directly connected to gluten are hormonal problems, manifesting as irregular menstrual cycles, sudden weight fluctuations, PMS, and sleep issues. Notably, hormonal imbalances caused by gluten intolerance can worsen during adolescence, pregnancy, and menopause, primarily affecting women.
“Neurological and Mental Health Implications”
Furthermore, gluten increases inflammation and permeability of the digestive tract, resulting in symptoms like concentration issues, depression, anxiety, insomnia, and fatigue. Importantly, some individuals with gluten intolerance experience irritability and a sense of easily losing focus and having an unhealthy obsession.
“Skin and Nail Manifestations”
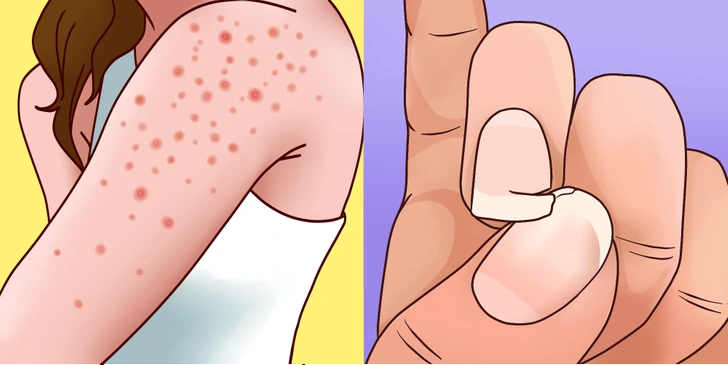
Conditions like hair keratosis and herpetiform dermatitis are directly linked to gluten intolerance, causing inflammation and rashes on various body parts. Additionally, weakened and brittle nails are also symptoms. Furthermore, other skin irritations like burn dermatitis may indicate gluten-induced issues.
“ADHD and Gluten Intolerance”
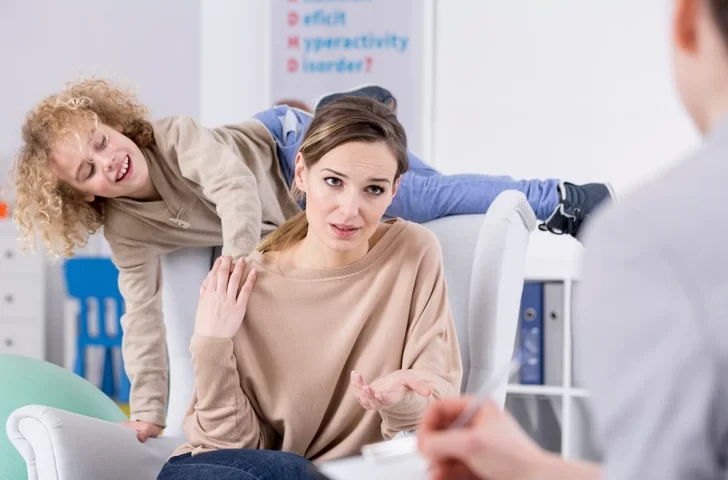

Another problem associated with gluten is attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), which affects both children and adults. Remarkably, individuals with ADHD may exhibit an attention deficit range and issues with self-control.
“Oral Health Concerns”
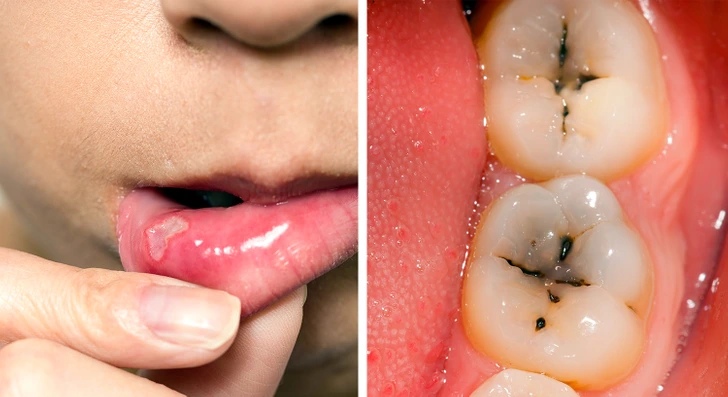
In the case of gluten intolerance, the absorption of essential elements and minerals in the digestive tract is impaired, including calcium. Consequently, this can result in teeth and oral cavity problems such as enamel sensitivity, tooth decay, cavities, and mucous membrane ulcers. Importantly, if oral issues arise despite proper dental care.
“Nutritional Deficiencies and Anemia”
Celiac disease is frequently diagnosed due to iron deficiency anemia. Symptoms include reduced blood volume, fatigue, shortness of breath, headaches, skin, and mucous membrane pallor, and even arthritis. Therefore, iron absorption is compromised with gluten intolerance, leading to poorly absorbable iron in the digestive system.
“Links to Autoimmune Diseases”
Specifically, celiac disease, an autoimmune disease, triggers the immune system to attack its digestive tract cells after gluten enters it. Consequently, this autoimmune disease increases the risk of developing other autoimmune diseases, including autoimmune thyroiditis, autoimmune liver disease, Crohn’s disease, diabetes, vitiligo, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis.
“Diagnosis and Treatment”
- Firstly, get tested by a doctor using a blood test for Celiac disease antibodies.
- Secondly, eliminate gluten from your diet by avoiding wheat, rye, bulgur, flour, semolina, and other foods. Always check product labels and prefer those labeled “gluten-free.”

[…] Gluten Intolerance: Recognizing and Conquering the Silent Culprit […]